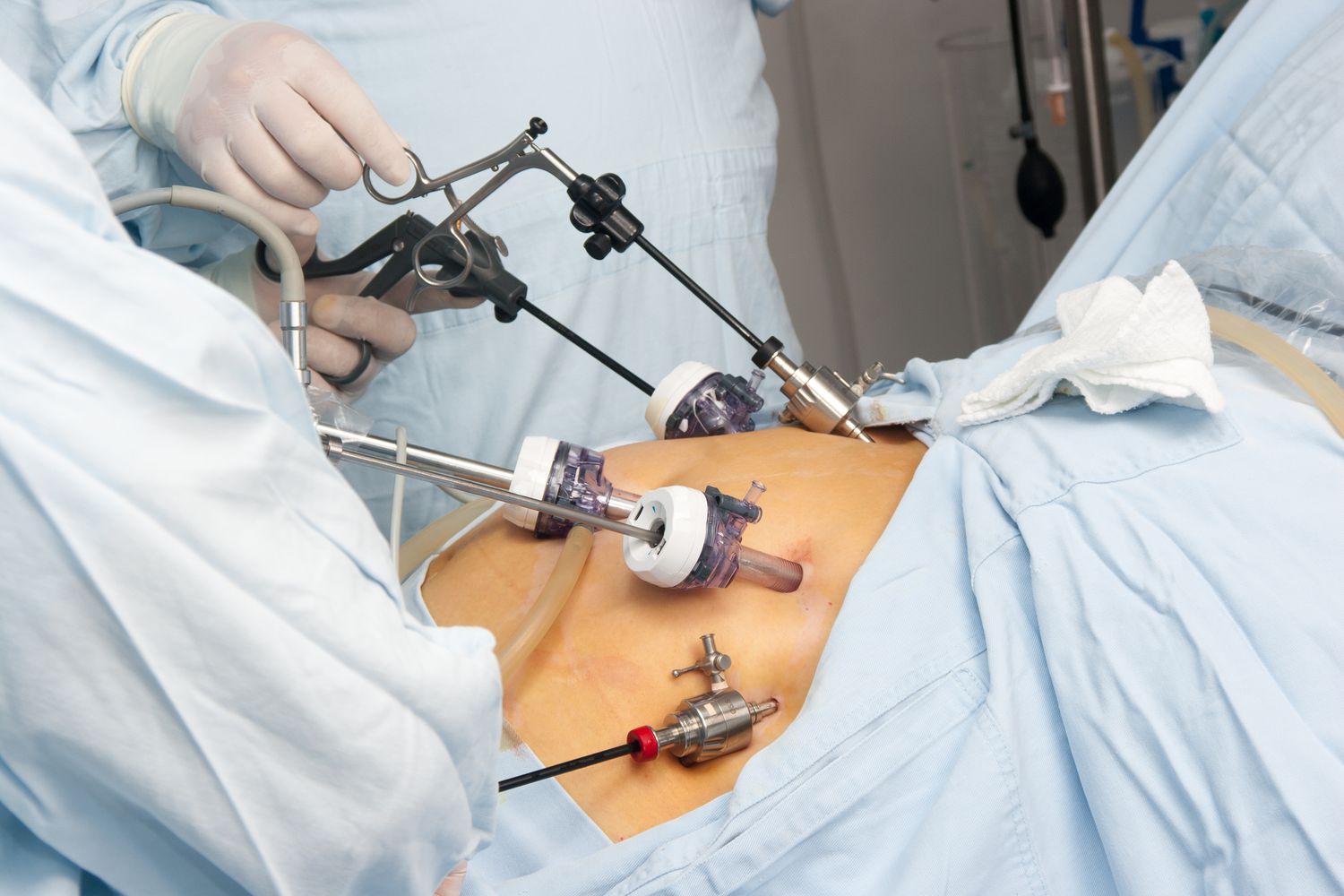
When talking about bariatric surgery it is referred to a set of fundamental interventions for obese people, both to eliminate excess adipose tissue and to prevent or treat pathologies associated with obesity. If, in fact, various therapies are possible to combat an overweight situation when one has to deal with significant obesity of the 2nd or 3rd degree, the only solution is bariatric surgery in India.
Obesity is a pathology caused by the increase in adipose tissue, which shortens life expectancy and worsens its quality since it is associated with various diseases of the metabolic type (type 2 diabetes, high cholesterol, and triglycerides ), cancer, and on the cardiovascular and respiratory systems.
Let’s go deeper into the topic in this blog.
Bariatric surgery: interventions
Bariatric surgery includes all those surgical interventions aimed at reducing weight in those suffering from obesity and treating the diseases associated with it.
They are minimally invasive operations carried out in laparoscopy: laparoscopy, combined with modern and effective management of the perioperative period, allows the patient to benefit from faster recovery, a short hospital stay, and a reduction in post-operative pain. Following a bariatric surgery in india, the patient must follow a long follow-up process to ensure the success of the operation through the maintenance of weight and the reduction of possible side effects of bariatric procedures.
Bariatric surgery provides, on average, a weight loss of 70% of the excess kilos, but the decrease can vary in relation to the age, height, gender, and medical history of the patient.
Cardiovascular diseases, respiratory insufficiency, and cancer: the consequences of obesity
Obesity can lead to the onset of pathologies such as:
- type 2 diabetes mellitus
- hypertension
- increase in blood cholesterol and triglycerides
- sleep apnea.
These disorders, both individually and combined and strengthening each other, can cause heart attack, stroke, and pulmonary embolism. Obesity is also a risk factor for respiratory insufficiency, osteoarthritis, and cancers such as those of the breast, uterus, colon, pancreas, and liver.
The purpose of bariatric surgery in india is twofold: weight loss and resolution or prevention of serious, long-term, even fatal, comorbidities that obesity entails.
Bariatric surgery: when to do the surgery?
Bariatric surgery is an option indicated for all people between the ages of 18 and 65 suffering from second-degree obesity (body mass index or BMI equal to or greater than 35) with associated diseases, such as type diabetes 2, arterial hypertension, sleep apnea, dyslipidemia, osteoarthritis or previous cardiovascular events, or third degree (body mass index or BMI equal to or greater than 40) even without associated diseases.
For those who have doubts about their body mass index, this is calculated by dividing the weight in kilos by the height in meters squared: for example, a person who weighs 120 kg and is 1.7 m tall will have a BMI of 41.5 (120 / 1.70 2 ). But if you have any doubts, you can easily find automatic BMI calculators on the Internet.
There are also some contraindications: bariatric surgery cannot be applied in the absence of previous conservative attempts (diet followed by a specialist), and in case of impossibility to collaborate in the follow-up for the best result of the operation: bariatric operations are therefore not recommended for those suffering from alcoholism, drug addiction, bulimia nervosa or decompensated psychosis.
Obesity: how to prevent it
Overweight patients must pay particular attention to preventing obesity by implementing a series of health strategies and rules. First of all, it is essential that those who are overweight change their lifestyle, making sure they exercise regularly and follow a healthy and balanced diet.
Today there are injection drugs (liraglutide, semaglutide, and, in the future, tripeptide), initially born for the treatment of diabetes but which have a powerful anti-hunger effect, which is able to make you lose 10 to 20 kilos of weight without causing hypoglycemia (as insulin and other anti-diabetic drugs can instead). Their use can greatly help overweight subjects prevent obesity: of course, the prescription of these drugs must take place within a diet.